Introduction
We encourage you to verify the source images for yourself, rather than just simply to accept the facts that are presented here.
Exact details of the used image templates can be found here.
Some reports on this website are based on previous ones. So it is extremely important to read the reports in chronological order.
Details can turn up that were probably already been analyzed in detail. If you are new here and you directly start reading the
recent reports without prior knowledge, then it could happen, that the required context is not recognizable.
You do yourself and us a favor when you first start with the oldest reports.
This report makes reference to structural anomalies in Aram Chaos. We recommend that you first review the previous reports from this series,
if you have not read them yet.
These include the following documents:
| Mars Global Surveyor (MGS)
|
Launched:
07.11.1996 |
Official Mars exploration started:
March 1999 |
Contact termination:
02.11.2006 |

Mars Global Surveyor © NASA/JPL
More than 200,000 images. That's the amount of the footage, the Mars probe "Mars Global Surveyor" delivered during its service life.
A wide range of interesting and high-resolution images were made which are, among other things, the foundation for this project.
From the meta-information of the images (see link to the MGS image archive) it turns out that the camera aboard MGS occasionally produced
images at a maximum resolution up to 1.5 meters per pixel.
The space probe had reached its planned service life in 2001, but the operting time was extended by NASA. Due to this, MGS was useful to be used
as a relay station for the two Mars Lander, Spirit and Opportunity, which reached Mars in early 2004. The contact with the probe unfortunately
broke in late 2006, so this source dried up.
The yield of the years of exploration by MGS can be evaluated on the following website.
Link: Malin Space Science Systems (MSSS)
Two image segments from the image series of Mars Orbiter Camera (MOC).
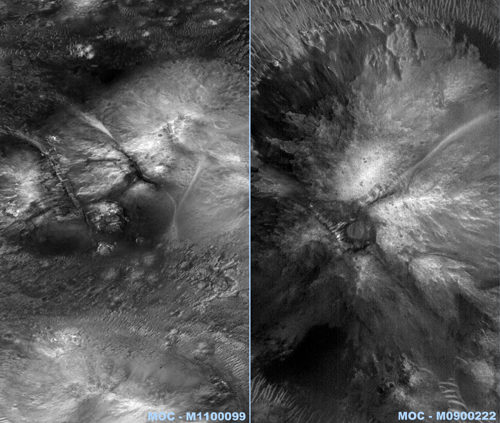

Click on image to enlarge
These images are particularly valuable in so far as strucural anomalies are almost instantly recognizable here.
| Mars Odyssey (MO)
|
Launched:
24.10.2001 |
Official Mars exploration started:
Februar 2002 |
Mission termination:
open |

Mars Odyssey © NASA
The spacecraft Mars Odyssey is equipped, among other things, with a special camera that is capable of taking images in the visible and infrared
part of the electromagnetic spectrum. In the visible wavelength range the socalled THEMIS (Thermal Emission Imaging System) camera can still disolve
structures with a size of about 18 meters. That is a much lower
resolution than the camera of Mars Global Surveyor. However, it should be noted that for the set mission objective, the resolution completely conform
to the requirements. The primary mission objective lies in the geologic record of the volcanic environment and the aftermath of traces of past
watercourses on Mars.
An inquiry in the image archive of Mars Odyssey is available on the following web site:
Link:
Mars Odyssey Mission - Arizona State University
THEMIS image sections from the corresponding recordings of Aram Chaos
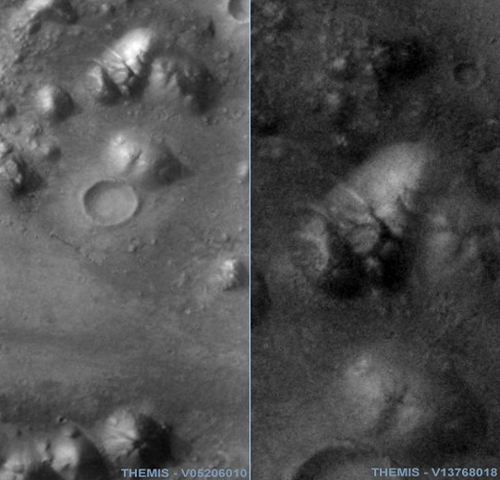

Click on image to enlarge
The picture above shows a selection of excerpts of the best recordings that exist regarding the ATLAS station. The remaining existing
images show the corresponding target area only from a much greater distance. Details can not be longer recognized in these images.
These pictures are far away from the quality of the MOC camera on Mars Global Surveyor space probe.
| Mars Express (MEX)
|
Launched:
02.06.2003 |
Official Mars exploration started:
January 2004 |
Mission termination:
open |
Mars Express © ESA
In March 2006, the space probe Mars Express has reached Mars. Its primary goal is the complete mapping of the Martian surface.
Equipped with a High Resolution Stereo Camera (HRSC) it delivers images with a resolution of
up to 10 meters and is also capable of creating colored 3D images. Such a resolution is not suitable
to make small details visible.
Interestingly, the HRSC owns a Super Resolution Channel (SRC) optic.
The theoretical resolution in this case is nearly 2 meters. However, technical problems seem to limit the use of the SRC significantly.
Nevertheless, even the regular shooting from Aram Chaos would be of interest for the analysis work. By this means, it would be possible to
get an general impression of the area around the station ATLAS. Under certain circumstances even at a resolution of 10 meters per pixel
one could gain useful information.
The Free University of Berlin provides with the application HRSCView a web-based interface for users that allows to access the Mars Express
HRSC image archive. The following link leads directly to this web interface and has been preset to
show the visitor almost exactly the structure that is referred here to as the ATLAS base.
Link:
HRSCview - with preset coordinates to bring you directly to the ATLAS-station
It's a pity that we must always expect ugly image transmission errors in Mars images...
Within these interference patterns is the anomaly we call the ATLAS base.
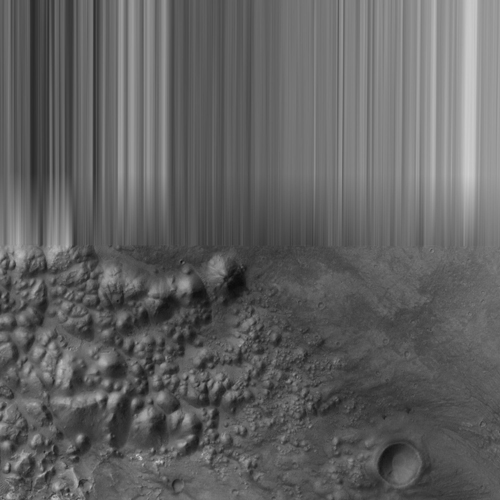

Click on image to enlarge
The shown error in the image above existed at least since the time we looked the first time at this area of Aram Chaos via
HRSC view. The error still exists up to the present time on which this report was written.
Nevertheless, the shown image section is a good example to make clear what value a high resolution can have. In
the center, directly under the bar of interference, is the "mountain" with the striking anomaly on its tip
which is only clearly visible on the recordings of "Mars Global Surveyor." Striking, interesting structures
are no longer recognizable here.
Perhaps it will eventually succeed, to take new, trouble-free images from this region, which also have improved
Meters / Pixel resolution.
| Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO)
|
Launched:
12.08.2005 |
Official Mars exploration started:
November 2006 |
Mission termination:
open |

Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter © NASA
At an altitude of 300 kilometers the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter is capable of taking images at a maximum vertical
resolution of 20-30 cm per pixel. The resolution of the HiRISE camera is an outstanding feature of the MRO space probe,
in terms of planetary science performance, which is only surpassed by modern military spy satellites.
Such a resolution wouldn't hardly leave any open questions, but only if the areas of interest are included.
The University of Arizona, which has ordered the construction of the camera, provides a website that allows to query the
HiRISE database for so far available images.
Link:
High Resolution Imaging Science Projekt - Lunar and Planetary Laboratory
At present, however, no pictures are available, showing the corresponding region in Aram Chaos. The HiRISE catalog shows that there are
images from Aram Chaos, but from areas not in close proximity to our discovered anomalies.
The following table summarizes all the facts that are of vital importance for our analytical work.
As target area we have focused on a structural abnormality, which we have called in our previous reports the ATLAS station.
| Space Probe |
Maximum Resolution |
Target Area
mapped? |
| Mars Global Surveyor (MGS) |
max. up to 1.5 meters/pixel |
yes |
| Mars Odyssey (MO) |
max. up to 18 meters/pixel |
yes |
| Mars Express (MEX) |
max. up to 2 meters/pixel |
yes* |
| Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) |
max. up to 30 centimeters/pixel |
no |
| *not in high resolution |
The juxtaposition of the individual images shows that only the recording of the Mars Global Surveyor space probe from 2004 offer the
best recording of the structural anomaly of the "hollowed out" the mountain in Aram Chaos. It is not just that this recording is the
oldest one, it is also made by the oldest one of the space probes listed here.
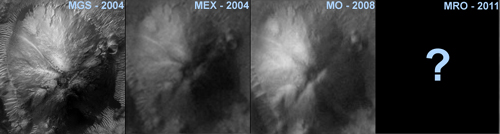
Click on image to enlarge
From the set of all available Mars images there is only one recording that shows the selected target area clearly with the relevant structures.
We must determine that no further recording is available that maps the corresponding area in high resolution.
Promising would be the shots of the HiRISE camera on the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter space probe.
|